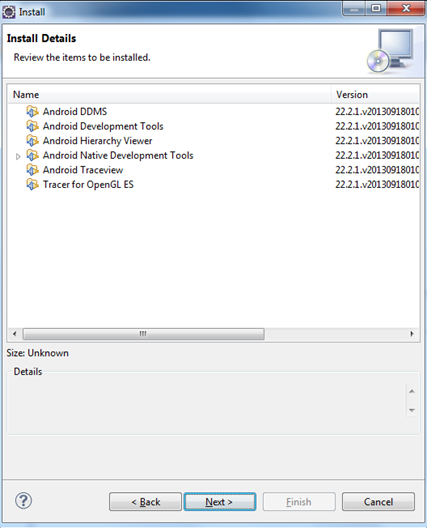
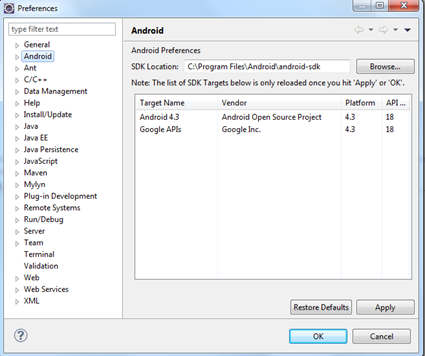
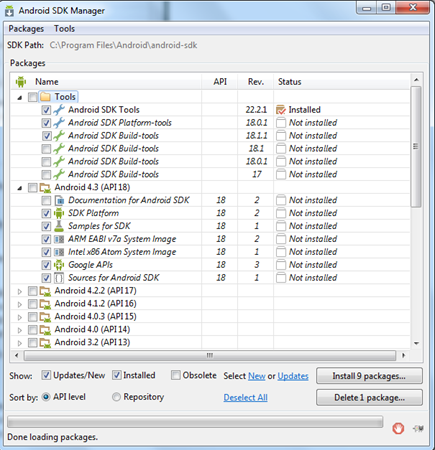
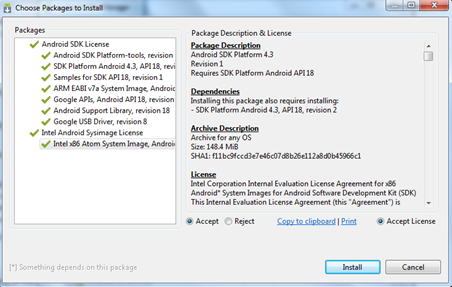
If you are a software developer you should at least write a “Hello World!” in android. That’s what we are going to do in this article. We know how android gets related to java and so to a java blog. Oops! I am not mentioning about the Oracle’s case against Google claiming the presence of java code in android.
As always, Hello World is the easiest step you can keep forward in learning a language. I would say, writing Hello World is not about learning the language. It is all about learning the setting up of the development environment, how to compile, interpret / execute.
IDE is everything in Hello, World
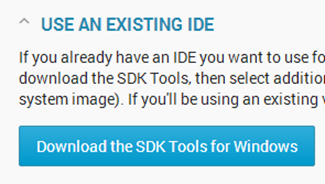
If you have completed setting up the development environment, then Android Hello World is simple. If you are using Eclipse as your IDE, setting up it for Android is also simple. Its about just installing a plugin. If you are not using Eclipse, don’t worry there are nice documentation available in android’s site.Android Hello World requires the following steps
- JDK 5 or above (JRE alone is not sufficient) installation
- Eclipse Ganymede or above installation
- Android SDK Installation
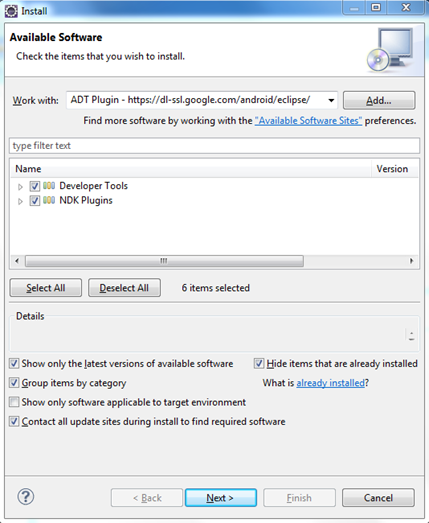
- Android Development Tools plugin installation
- Android Emulator – Android Virtual Device (AVD) Creation
- New Android Project Creation
- Create Hello World Android source
- Run Android Hello World
If you are a java guy, you should be already having some JDK installed in your computer. Just check the version for compatibility. If you have a older version of Eclipse, download the latest version. No harm in having multiple Eclipse versions. Android SDK and plugin installation, just follow the instructions given the URL I have given above. They are more than sufficient.
After you install the ADT plugin, restart the eclipse. Then in Eclipse, Window -> Preferences (in left panel select Android) then give your SDK installed location in the right side panel.
Android Emulator
If you have an android mobile and you want to execute your Hello World in that, there is a time for it. First master yourselves with the basics and you can use the Android Emulator. Always try first with the emulator before going to the real mobile. It will save you lot of time.
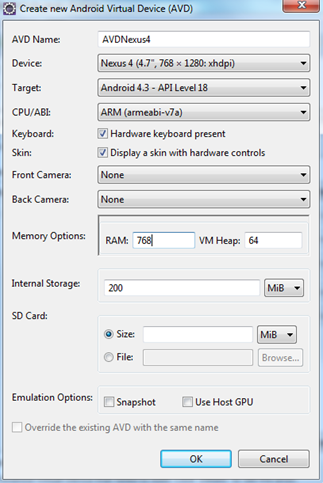
Click the android icon (with a white down arrow) from the Eclipse toolbar. I have show that icon in the below image. Then click the ‘New’ button and create a AVD. Finally it should look like the window in my image.
Android Hello World Project Creation
Right click in your Eclipse’s Package Explorer and New -> Android Project. Give a project name(Ex: AndroidHelloWorld), then select the Build Target. The build target should match the api version you have given at the time of AVD creation. Then fill the properties panel also.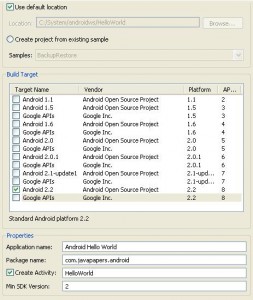
Now the HelloWorld android project is ready to use. Open the HelloWorld.java from the project source. You should have a HelloWorld class source code similar to the below.
package com.javapapers.android;import android.app.Activity;import android.os.Bundle;public class HelloWorld extends Activity { /** Called when the activity is first created. */ @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); }} |
Now lets add our HelloWorld part to it. Edit the code and add the following snipped to it. Import TextView also.
TextView tv = new TextView(this);tv.setText("Hello World!"); |
setContentView(tv); |
package com.javapapers.android;import android.app.Activity;import android.os.Bundle;import android.widget.TextView;public class HelloWorld extends Activity { /** Called when the activity is first created. */ @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); TextView tv = new TextView(this); tv.setText("Hello World!"); setContentView(R.layout.main); }} |
Run your Android Hello World App
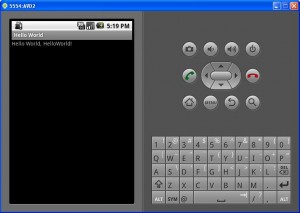
Right click on the project ‘Run As -> Android Application’The AVD (emulator) will get started and it will take a while to respond. AVD needs that time to initialize itself. Wait for 2 to 3 minutes. Keep an eye on the console, it will give you some background process status information. Then you see “Hello World!”
.